Mental health and gut health may seem like two unrelated aspects of our overall well-being, but growing scientific evidence reveals a strong connection between the two. The link between mental health and gut health is often referred to as the “gut-brain axis.” This connection highlights how the gut, sometimes called the “second brain,” plays a pivotal role in regulating mental health, emotions, and cognitive functions. In this article, we will explore the relationship between gut health and mental health, how gut bacteria impact our mood, and the ways you can improve both for better overall well-being. (Learn: How to reduce stress?)
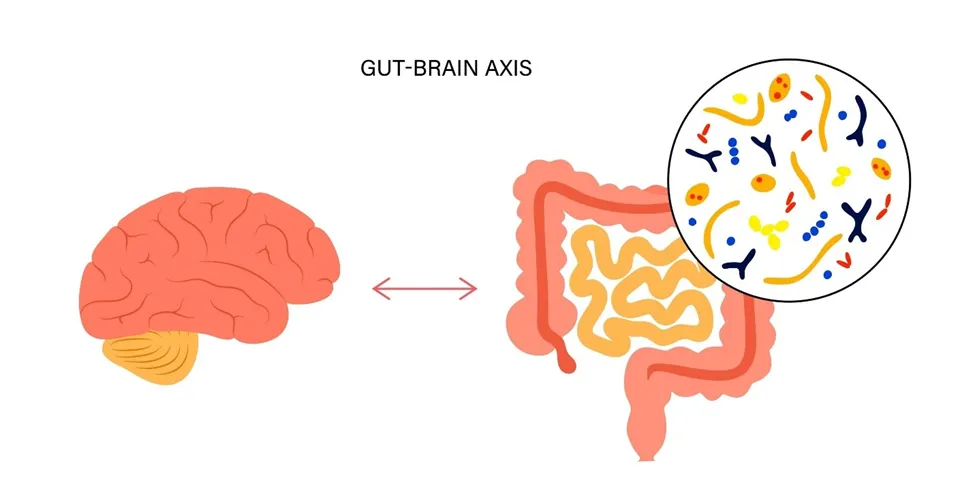
The Gut-Brain Connection
The gut-brain axis is a bi-directional communication network that links the gut to the brain. This pathway allows signals to travel from the gut to the brain and vice versa. The gut contains trillions of bacteria, collectively known as the gut microbiome, which can have a significant impact on the brain’s functions. These bacteria produce neurotransmitters and other chemicals that influence mood, anxiety, stress levels, and even cognition.
1. Gut Microbiome and Mental Health
Research has shown that the gut microbiome plays a crucial role in regulating mental health. The balance of good and bad bacteria in the gut can influence the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, both of which are important for mood regulation. In fact, about 90% of serotonin is produced in the gut, making it a central player in our emotional and mental state.
When the gut microbiome is in balance, it supports the production of these mood-regulating chemicals, promoting a sense of well-being. However, an imbalance in gut bacteria, known as dysbiosis, can lead to a range of mental health issues, including anxiety, depression, and even conditions like autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
2. How Gut Health Affects Mood and Anxiety
One of the key mechanisms by which gut health influences mental health is through the gut-brain axis. The vagus nerve, which runs from the brain to the gut, is a critical pathway for communication between the two organs. When the gut experiences inflammation or an imbalance in bacteria, it can send signals to the brain that can increase the risk of anxiety and depression.
Furthermore, the gut microbiome is involved in regulating the body’s stress response. A healthy microbiome can reduce the production of stress hormones like cortisol, while an unhealthy microbiome can exacerbate stress and anxiety.
The Role of Gut Bacteria in Mental Health
3. Gut Bacteria and Neurotransmitter Production
The gut microbiome is responsible for producing a variety of chemicals that influence the brain’s functioning. These include:
- Serotonin: As mentioned earlier, 90% of serotonin is produced in the gut. This neurotransmitter is crucial for mood regulation and feelings of happiness.
- Dopamine: Another important neurotransmitter, dopamine is involved in motivation, reward, and pleasure. It helps regulate mood and cognitive function.
- Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA): This neurotransmitter plays a key role in reducing anxiety and promoting relaxation.
A balanced gut microbiome produces these neurotransmitters in optimal amounts, supporting emotional stability and cognitive function. On the other hand, an imbalance in the gut microbiome can lead to disruptions in neurotransmitter production, contributing to mental health issues.
4. Inflammation and the Gut-Brain Axis
Inflammation in the gut can have profound effects on the brain and mental health. Chronic inflammation in the gut can result in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are chemicals that can enter the bloodstream and affect brain function. These cytokines can influence mood and may contribute to conditions like depression and anxiety.
Research suggests that people with mental health disorders often have higher levels of gut inflammation, and that reducing inflammation can improve symptoms of depression and anxiety.
How to Improve Gut Health for Better Mental Health
Since the health of your gut microbiome plays such an important role in your mental health, improving gut health is one of the best ways to support emotional well-being. Here are some practical ways to improve gut health:
5. Eat a Gut-Friendly Diet
A diet rich in fiber, prebiotics, and probiotics is essential for maintaining a healthy gut microbiome. Foods that support gut health include:
- Fiber-rich foods: Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes provide prebiotics, which feed beneficial bacteria in the gut.
- Fermented foods: Foods like yogurt, kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, and miso contain probiotics, which are live beneficial bacteria that can help restore balance to the gut microbiome.
- Healthy fats: Omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts have anti-inflammatory properties that can benefit both gut and brain health.
6. Manage Stress Effectively
Chronic stress is one of the biggest contributors to an imbalanced gut microbiome. Stress activates the body’s fight-or-flight response, which can disrupt gut bacteria and increase gut inflammation. To manage stress effectively, consider incorporating relaxation techniques such as:
- Mindfulness and meditation
- Deep breathing exercises
- Yoga or Tai Chi
- Physical exercise
By reducing stress, you can help maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria and improve overall mental health.
7. Get Enough Sleep
Sleep is crucial for both gut and mental health. Studies have shown that poor sleep can disrupt the gut microbiome, while a healthy gut can improve sleep quality. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to support both gut health and mental well-being.
8. Avoid Overuse of Antibiotics
Antibiotics can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, often killing off both harmful and beneficial bacteria. While antibiotics are necessary for treating certain infections, they should be used only when prescribed by a healthcare professional. Overuse or misuse of antibiotics can lead to dysbiosis and negatively affect mental health.
9. Consider Supplements for Gut Health
Probiotics and prebiotic supplements can help support a healthy gut microbiome. Probiotics introduce beneficial bacteria to the gut, while prebiotics provide food for those bacteria. However, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional before adding supplements to your routine to ensure they are suitable for your needs.
Mental Health Disorders Linked to Gut Health Imbalance
Several mental health disorders have been linked to an imbalance in gut health, including:
- Depression: Dysbiosis and gut inflammation have been linked to increased levels of depression. Studies have shown that improving gut health with probiotics can alleviate some symptoms of depression.
- Anxiety: An imbalance in gut bacteria can exacerbate anxiety disorders. Restoring gut balance may help reduce anxiety levels.
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): Some research suggests that children with ASD may have a different gut microbiome composition, which may contribute to behavioral symptoms. Though the relationship is not fully understood, improving gut health may play a role in managing symptoms.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): IBS is a digestive disorder that has been closely linked to mental health conditions like anxiety and depression. Addressing both the gut and mental health components of IBS can improve symptoms and quality of life.
Conclusion: The Importance of Mental and Gut Health Interdependence
The growing body of research on the link between mental health and gut health underscores the critical relationship between these two aspects of well-being. The gut-brain axis demonstrates that the health of your gut can directly impact your mental health, and vice versa. By adopting a healthy diet, managing stress, prioritizing sleep, and using probiotics or prebiotics as needed, you can improve both your gut and mental health.
Taking care of your gut microbiome is not only essential for digestion but also for maintaining a stable and positive mental state. Whether you’re dealing with anxiety, depression, or other mental health challenges, understanding the link between mental health and gut health is the first step toward improving your overall quality of life.
Final Takeaway: Invest in Your Gut, Boost Your Mental Health
In summary, mental health and gut health are deeply connected through the gut-brain axis. A balanced gut microbiome is essential for emotional well-being, cognitive function, and managing stress. By nourishing your gut with the right foods, reducing stress, getting enough sleep, and considering probiotics, you can optimize both your gut health and mental health for a happier, healthier life.
FAQs: Understanding the Link Between Mental Health and Gut Health
1. What is the gut-brain axis?
The gut-brain axis refers to the communication system that connects the gut and the brain. This bi-directional pathway allows signals to travel from the gut to the brain and vice versa, influencing mood, emotions, cognition, and overall mental health. The gut microbiome, which is made up of trillions of bacteria, plays a central role in this communication.
2. Can gut health really affect my mental health?
Yes, there is a growing body of research showing that the health of your gut can significantly impact your mental health. An imbalance in the gut microbiome (known as dysbiosis) has been linked to mental health conditions like anxiety, depression, and stress. A healthy gut microbiome supports the production of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, which regulate mood and emotions.
3. How does gut bacteria influence my mood?
Gut bacteria produce essential chemicals, including serotonin, which plays a key role in mood regulation. In fact, about 90% of serotonin is made in the gut. Imbalances in gut bacteria can disrupt the production of these mood-regulating chemicals, potentially leading to symptoms of anxiety, depression, or irritability.
4. Can I improve my mental health by improving my gut health?
Yes, improving gut health can have a positive impact on mental health. A balanced diet rich in fiber, prebiotics, and probiotics supports the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, which in turn supports better mental health. Managing stress, getting enough sleep, and avoiding excessive antibiotic use also contribute to a healthy gut and improved mood.
5. What foods should I eat to improve my gut and mental health?
To improve both gut and mental health, include the following in your diet:
- Fiber-rich foods: Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes provide prebiotics, which feed beneficial bacteria.
- Fermented foods: Foods like yogurt, kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, and miso contain probiotics that promote a healthy microbiome.
- Healthy fats: Omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts help reduce inflammation in both the gut and the brain.
- Antioxidant-rich foods: Berries, leafy greens, and nuts can reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in the body.
6. Can stress harm my gut health?
Yes, chronic stress can negatively impact gut health by increasing gut inflammation and disrupting the balance of gut bacteria. When you’re stressed, the body releases cortisol and other stress hormones, which can damage the gut lining and contribute to conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Managing stress effectively through practices like yoga, meditation, and exercise can help protect gut health.
7. Is there a connection between gut health and conditions like anxiety and depression?
Yes, studies have shown that an imbalance in gut bacteria can contribute to mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression. The gut microbiome influences the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which regulate mood and emotional health. Restoring balance to the gut microbiome can alleviate some symptoms of these conditions.
8. Can probiotics help with mental health issues?
Probiotics may help improve mental health by restoring balance to the gut microbiome. Certain strains of probiotics have been shown to reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression, likely due to their positive effects on neurotransmitter production and inflammation. However, it’s always best to consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements.
9. How can poor gut health affect sleep?
Poor gut health can interfere with sleep by disrupting the production of serotonin and melatonin, both of which regulate sleep cycles. Imbalances in gut bacteria can lead to sleep disturbances and poor-quality sleep. Conversely, improving gut health may help improve sleep patterns and overall sleep quality.
10. How long does it take to see improvements in mental health after improving gut health?
The timeline for improvements can vary, but many people start to notice changes in mood and mental clarity within a few weeks of adopting gut-healthy practices like a balanced diet, reducing stress, and using probiotics. However, significant improvements may take a few months, as the gut microbiome can take time to restore balance.
11. Is it safe to take probiotics for gut and mental health?
In general, probiotics are safe for most people, but it’s important to choose the right strains for your specific needs. It’s recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before starting probiotics, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medication. A healthcare provider can help you determine the best probiotic strain for your gut and mental health.
12. Can an unhealthy gut make mental health problems worse?
Yes, an unhealthy gut with an imbalanced microbiome can exacerbate existing mental health problems. Conditions like depression, anxiety, and stress may worsen if the gut’s balance is disrupted. This is why maintaining a healthy gut is vital for supporting emotional stability and mental well-being.
13. Can a bad diet lead to mental health issues?
Yes, a poor diet—especially one high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats—can negatively impact the gut microbiome, leading to inflammation and dysbiosis. This imbalance in gut bacteria may contribute to mental health issues such as anxiety and depression. A balanced diet that includes fiber, fermented foods, and healthy fats is essential for maintaining both gut and mental health.
14. What is the role of inflammation in gut health and mental health?
Chronic inflammation in the gut can affect brain function and has been linked to mental health issues like anxiety and depression. Inflammatory molecules can travel from the gut into the bloodstream and affect the brain, causing mood disruptions. Reducing inflammation through diet, exercise, and stress management can improve both gut and mental health.
15. Can mental health conditions like depression cause gut problems?
Yes, mental health conditions such as depression can contribute to digestive issues. Depression is often associated with gastrointestinal disturbances like bloating, constipation, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Additionally, stress and anxiety, which often accompany depression, can exacerbate gut problems. Addressing both mental health and gut health is important for managing these symptoms.
Visit: youtubpremiummodapk.com

